Food Processing Methods
Food Processing
Food processing is to turn fresh foods into processed food products.This can involve one or combination of various processes including washing, chopping, pasteurizing, freezing, fermenting, packaging, cooking and many more.Food processing also includes adding ingredients to food, for example to extend shelf life.
Methods of Food Processing
Food processing includes traditional methods,
Heat treatment
Fermentation( pickling)
Smoking
Drying
Pasteurization
High pressure processing
Freezing
Modified atmosphere packaging
Canning
Heat treatment
Heating food is an effective way of preserving. The basic purpose for the thermal processing of foods is, to reduce or destroy microbial activity, reduce or destroy enzyme activity, and to produce physical or chemical changes, to make the food meet a certain quality standard.
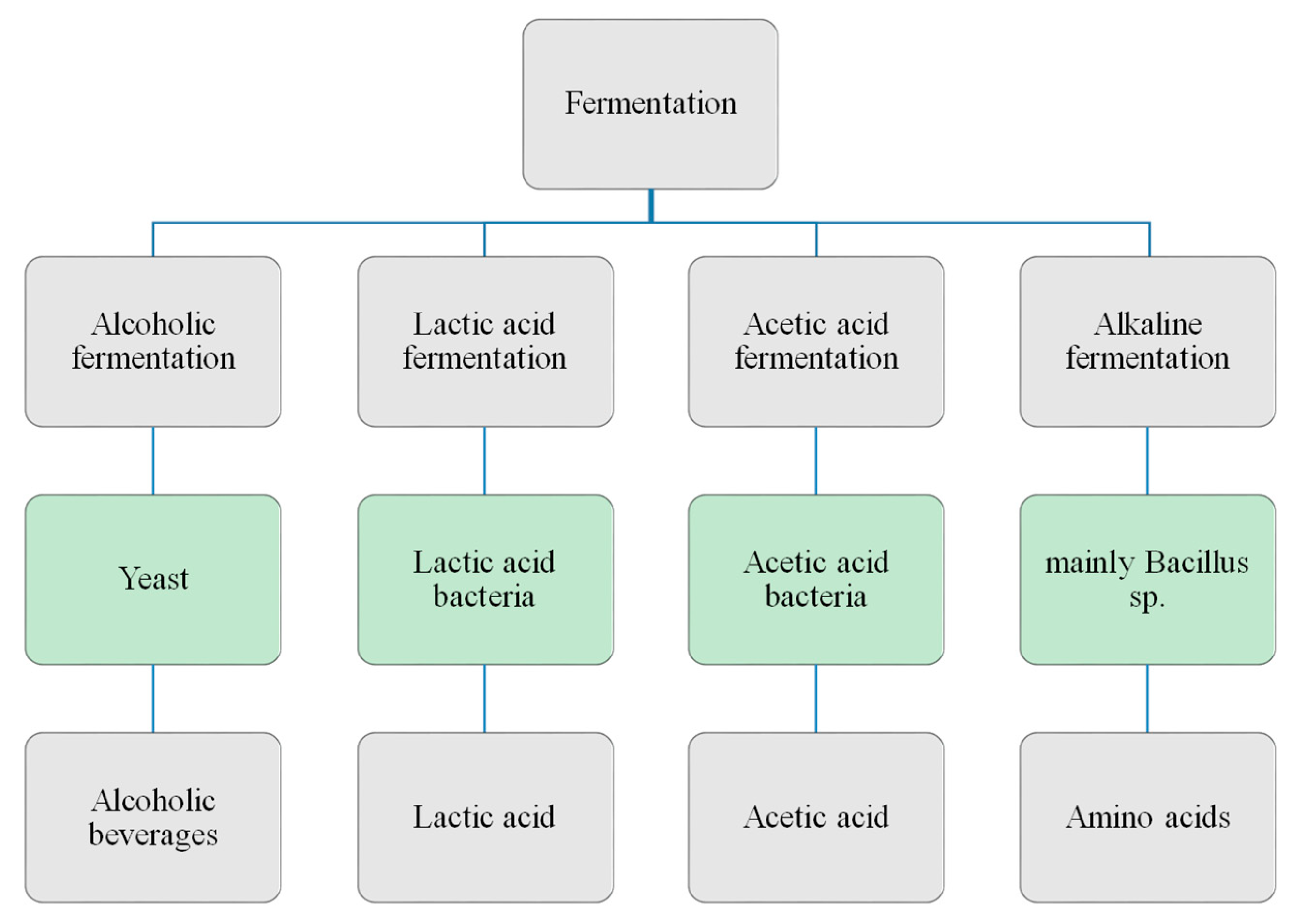
Fermentation
The breakdown of sugars by bacteria, yeasts or other microorganisms under anaerobic conditions. This means, no oxygen is needed for the process to take place (apart from oxygen present in sugar). Fermentation is notably used in the making of alcoholic beverages such as wine, beer, and cider, and in the preservation of foods such as sauerkraut, dry sausages, and yogurt, but also for raising dough in bread production.
Smoking
A process of heat and chemical treatment of food to help preserve it by exposing it to smoke from burning material such as wood. Smoked foods usually include types of meat, sausages, fish or cheese.
Drying
Pasteurisation
Food is heated and then quickly cooled down to kill microorganisms. For example, raw milk may contain harmful bacteria that cause food-borne illnesses. Boiling it (at home) or pasteurizing (on a large scale) is crucial to ensure it is safe to consume. Apart from dairy products, pasteurization is widely used in preservation of canned foods, juices and alcoholic beverages.
Ultra-heat treatment
Ultra-heat treatment
Freezing
High pressure processing
High pressure processing (HPP) is a promising “non-thermal” technique for food preservation that efficiently inactivates the vegetative microorganisms, most commonly related to food-borne diseases allowing most foods to be preserved with minimal effect on taste, texture or nutritional characteristics.
Modified atmosphere packaging
Air inside a package is substituted by a protective gas mix, often including oxygen, carbon dioxide and nitrogen – gases that are also present in the air we breathe. They help to extend the shelf life of fresh food products - usually of fruits, vegetables, meat and meat products, and seafood.
The food is heated to a high temperature. This process is called pasteurisation. Then, the food is packaged and stored in an air-tight can. Check our infographic showing the processing steps for canned tomatoes.
Reasons of food processing
Makes food edible
Grain crops, for example wheat and corn, are not edible in their natural state. Processing techniques, such as milling and grinding, turn them into flour, after which they can be made into breads, cereals, pasta and other edible grain-based products. There are 3 types of flours depending on the processing level, choose wholegrain when possible. You can learn more about the journey of grain to bread in our ‘Gain on grain’ info-graphic.
Safety, shelf life, and preservation
Processing improves or even ensures food safety by removing harmful microorganisms. The main methods are pasteurization, air-tight packaging, and the use of preservatives.
Nutritional quality
Food processing can affect the nutritional quality of foods in both ways: it can enhance it, for instance by adding components that were not present, like vitamin D (through ‘fortification’), or by lowering fat, salt or sugar. It can also cause some fiber and vitamins and minerals to be lost, for example through excessive refining, heating or freezing.
Convenience
Processing and packaging technologies help to answer modern day time-constraints by providing a range of convenient foods: ready meals, bagged salads, sliced and canned fruits and vegetables that take little time to prepare and can be consumed “on the go”.
Price
Food processing can decrease the cost of foods. For example, frozen vegetables have a similar nutritional value as fresh ones, but at a lower price, as they have already been prepared, do not contain inedible parts, can be bought in bulk, and can last longer. This way, processing increases the shelf life of food, and decreases the amount of waste, reducing thereby the overall costs of food production.
How does processed food fit into a healthy diet?
A healthy diet means eating a variety of nutritious foods from different food groups, including fresh fruits and vegetables, grains and cereals (opting for whole grains when possible), proteins, dairy and healthy fats. Most foods consumed nowadays are processed at least to some degree, but not all processed foods are the same. For example, fruit canned in fruit juice will be a better option than fruit canned in a sugary syrup. Therefore, when chosen mindfully, processed foods can be incorporated into a healthy and balanced diet.
Less processed foods such as frozen fruits and vegetables provide valuable sources of nutrition, with greater convenience and lower price. Chopped, frozen, and canned foods in natural juices are good alternatives for busy people having limited time to shop for or cook from a fresh produce.
Some processed foods that contain less fiber, and higher levels of (saturated) fat, added sugar and salt, are best consumed occasionally.





Good effort
ReplyDeleteGood techniques but may be in shown in video
ReplyDeleteGreat information about Modified Atmosphere Packaging
ReplyDeletethanks for your comments
ReplyDelete